- Timing: 24/7 Avaiable
- Call us: +91 9637257670 , +91 9518519369
- Timing: 8:30 am to 6:00 pm
- Call us: +91 9822827576
Call us: +91 9370881414
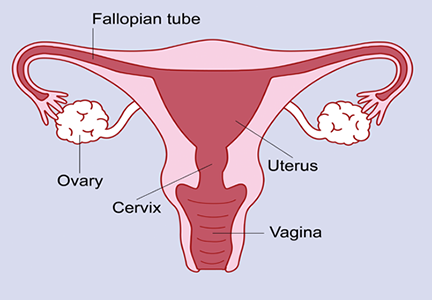
Surgery involving the uterus and ovaries can be necessary to treat various gynecological conditions, such as fibroids, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and gynecological cancers.