- Timing: 24/7 Avaiable
- Call us: +91 9637257670 , +91 9518519369
- Timing: 8:30 am to 6:00 pm
- Call us: +91 9822827576
Call us: +91 9370881414
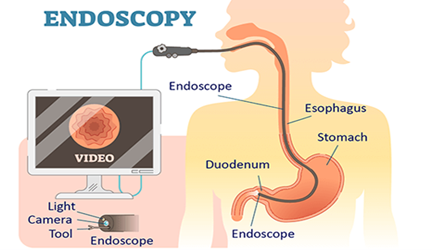
Gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows a healthcare provider to examine the inside of the gastrointestinal tract using an endoscope. An endoscope is a flexible tube with a light and camera on the end that provides a view of the GI tract on a monitor. GI endoscopy can help diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the upper and lower GI tract.